Open Source Air-Bearing Simulation
The analytical and numerical simulation of air bearings has been a field of research for a long time. As such, the history and various methods and approaches are well documented in the literature [1]. However, their implementation requires considerable knowledge of numerical mathematics and coding. Another option is multi- physics software such as COMSOL. It is being used for air-bearing simulation [2] [3]. We found that quite some modeling effort is necessary to achieve good results. Especially for micro-groove and restrictor-regulated bearings and subsequent model fitting, customization is required. While certainly an option to consider for many applications, there are drawbacks to using a small part of a large software suite to analyze a narrowly defined problem. One example is the licensing cost. Combined, there might be a barrier to entry for some and a significant time investment for others to simulate an air bearing. It could be speculated, that considerable duplicative effort has been made to model or write what is essentially the same software, by researchers the world over. The air bearing simulation described here does not claim to be novel in the modeling approach, but rather in the fact that it is an open-source project with accessibility and modularity in mind. Eitzenberger will release the first version of the simulation on Github by the end of 2024, hoping that others will find it helpful, and will consider joining the collaborative development.
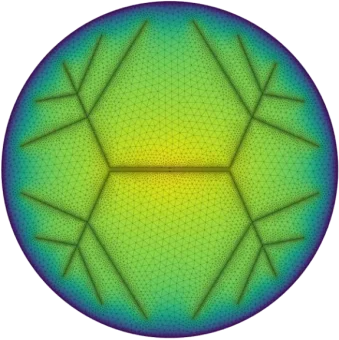
Pressure distribution of an Eitzenberger nozzle and micro-groove regulated air bearing at a given air gap.
Fahrsimulator


7-Achs-System

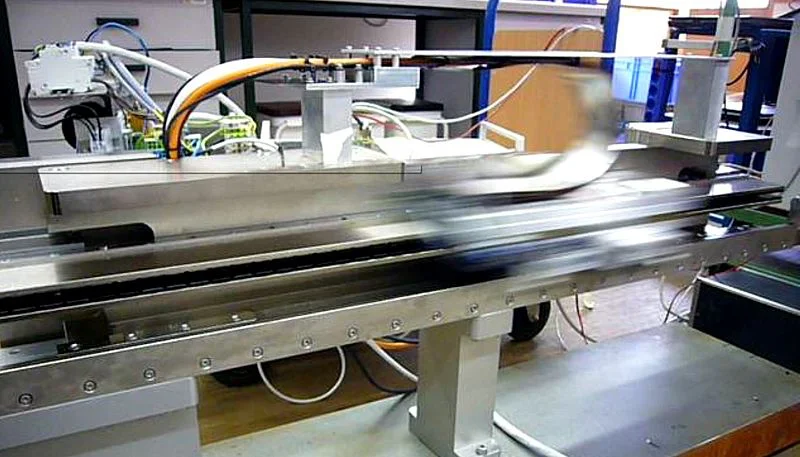
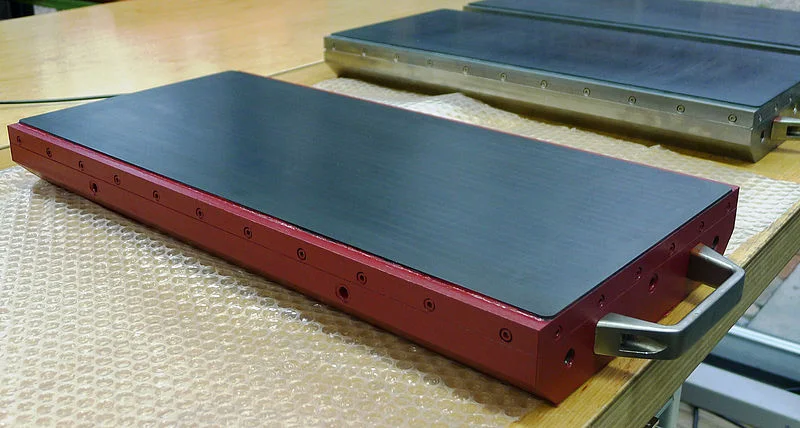
Rolling Road und Conveyor



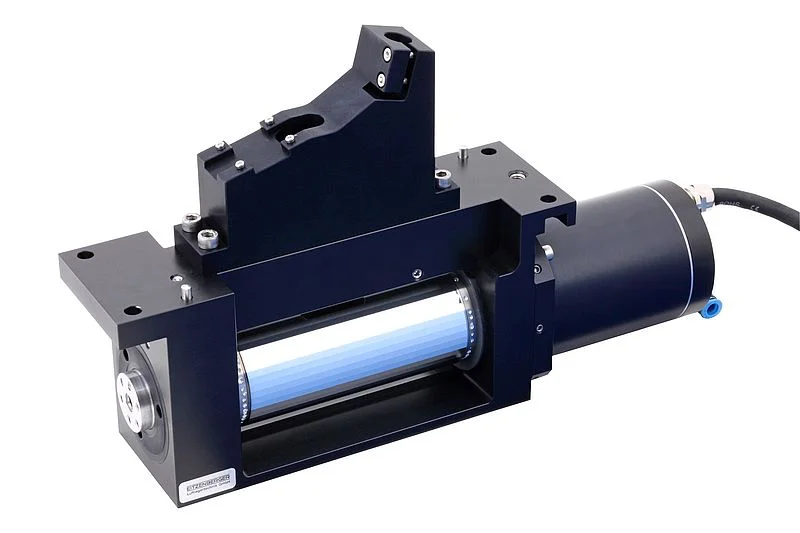
Polygon-Scanner
Die luftgelagerte Scannerachse ist für eine Drehzahl von bis zu 60 000 U/min ausgelegt. Durch die Luftlagerung ist sie verschleißfrei. Zylindrizitätsfehler der Polygonfacetten < 1 µm.

Fast-Tool
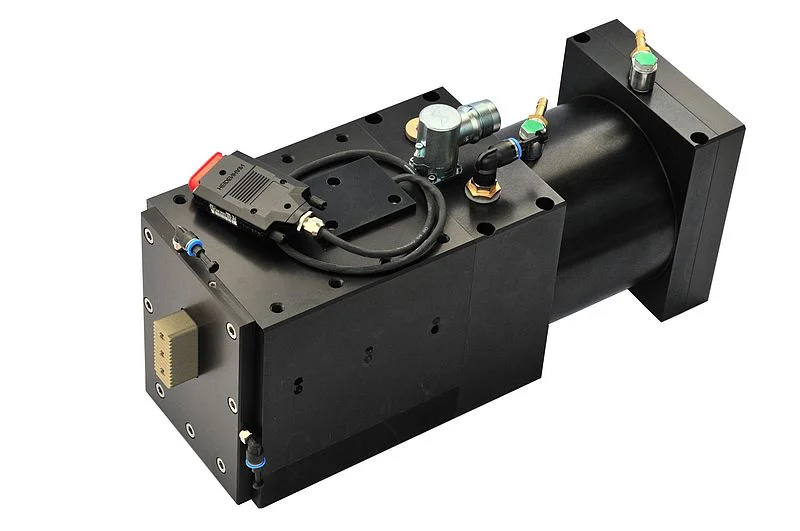

Hochgeschwindigkeits-Linearachse
Luftgelagerte Hochgeschwindigkeitsachse, Hub 600 mm, Geschwindigkeit 8 m/s. Beschleunigung 180 m/s2, Wiederholgenauigkeit 0,2 µm. Die Achse eignet sich für schnelle und präzise Pick-and-Place Anwendungen im Halbleiterbereich.

